
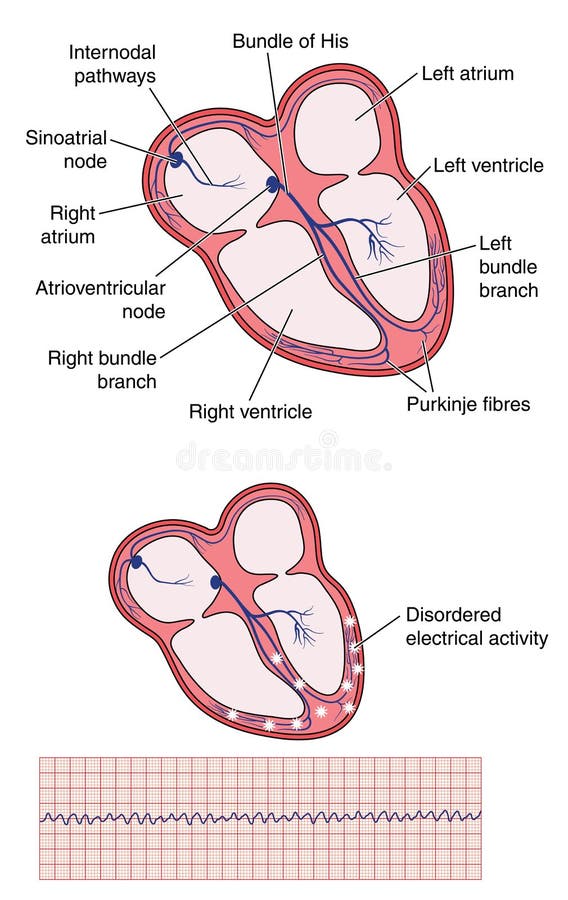
The ST segment corresponds to the plateau phase (phase 2) of the action potential. Wide (also referred to as broad) QRS complexes indicate that ventricular depolarization is slow, which may be due to dysfunction in the conduction system.

A short QRS complex is desirable as it proves that the ventricles are depolarized rapidly, which in turn implies that the conduction system functions properly. QRS duration is the time interval from the onset to the end of the QRS complex. Since the electrical vector generated by the left ventricle is many times larger than the vector generated by the right ventricle, the QRS complex is actually a reflection of left ventricular depolarization. It is always referred to as the “QRS complex” although it may not always display all three waves. The QRS complex represents the depolarization (activation) of the ventricles. The amplitude of any deflection/wave is measured by using the PR segment as the baseline. The PR segment serves as the baseline (also referred to as reference line or isoelectric line) of the ECG curve. The flat line between the end of the P-wave and the onset of the QRS complex is called the PR segment and it reflects the slow impulse conduction through the atrioventricular node. The PR interval is assessed in order to determine whether impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles is normal. The PR interval is the distance between the onset of the P-wave to the onset of the QRS complex. The P-wave reflects atrial depolarization (activation). The P-wave, PR interval and PR segmentĮCG interpretation traditionally starts with an assessment of the P-wave.

ECG interpretation requires knowledge of these waves and intervals. Important intervals and points of measurement are depicted. The classical ECG curve with its most common waveforms. Relative to the R-waves, T-waves are too large and pointed (differential diagnoses are considered below). Relatively large T-waves in V2-V3, with ST-segment elevations. Slight ST-segment elevation in leads V2-V3, which is normal in men and women. Sinus rhythm, rapid progression of R-waves in precordial leads. Discrete ST-segment depressions in leads V5-V6. R-waves have low amplitude, suggesting low voltage (see below).

Also note that this chapter is accompanied by a video lecture: Video lecture: The Normal ECG, which covers all topics discussed below.
#Ventricular fibrillation pulseless electrical activity ecg how to#
Thus, in this chapter, you will learn the physiological basis of all ECG waves and how to determine whether the ECG is normal or abnormal. Although heart rhythm will be discussed in detail in the next chapters, fundamental aspects of rhythm will also be covered in this discussion (refer to Normal Rhythm and Arrhythmias). A rather extensive discussion is provided in order to give the reader firm knowledge of normal findings, normal variants (i.e less common variants of what is considered normal) and pathological variants. This chapter will focus on the ECG waves in terms of morphology (appearance), durations and intervals. At the heart of ECG interpretation lies the ability to determine whether the ECG waves and intervals are normal. This is arguably one of the most important chapters throughout this course. ECG Interpretation Part 1: definitions, criteria, and characteristics of the normal ECG (EKG) waves, intervals, durations & rhythm


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
